Mechanical Engineering Wiki / Plastic Welding
Plastic welding - joining process for plastics
Plastic welding is a joining process in which two plastic components are permanently joined together. Plastic welding is an alternative to other joining processes such as gluing or soldering. Plastic welding is mainly used for plastics that cannot be glued together or can only be glued together insufficiently. This applies, for example, to polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyethylene (PE). It is important for the connection using plastic welding that the plastics have thermoplastic properties. This means that they can be melted (repeatedly) and then solidify again. Different processes are used for plastic welding depending on the material and the target specification. In addition, certain ambient temperatures must be maintained depending on the plastic to be welded.
The different types of plastic welding
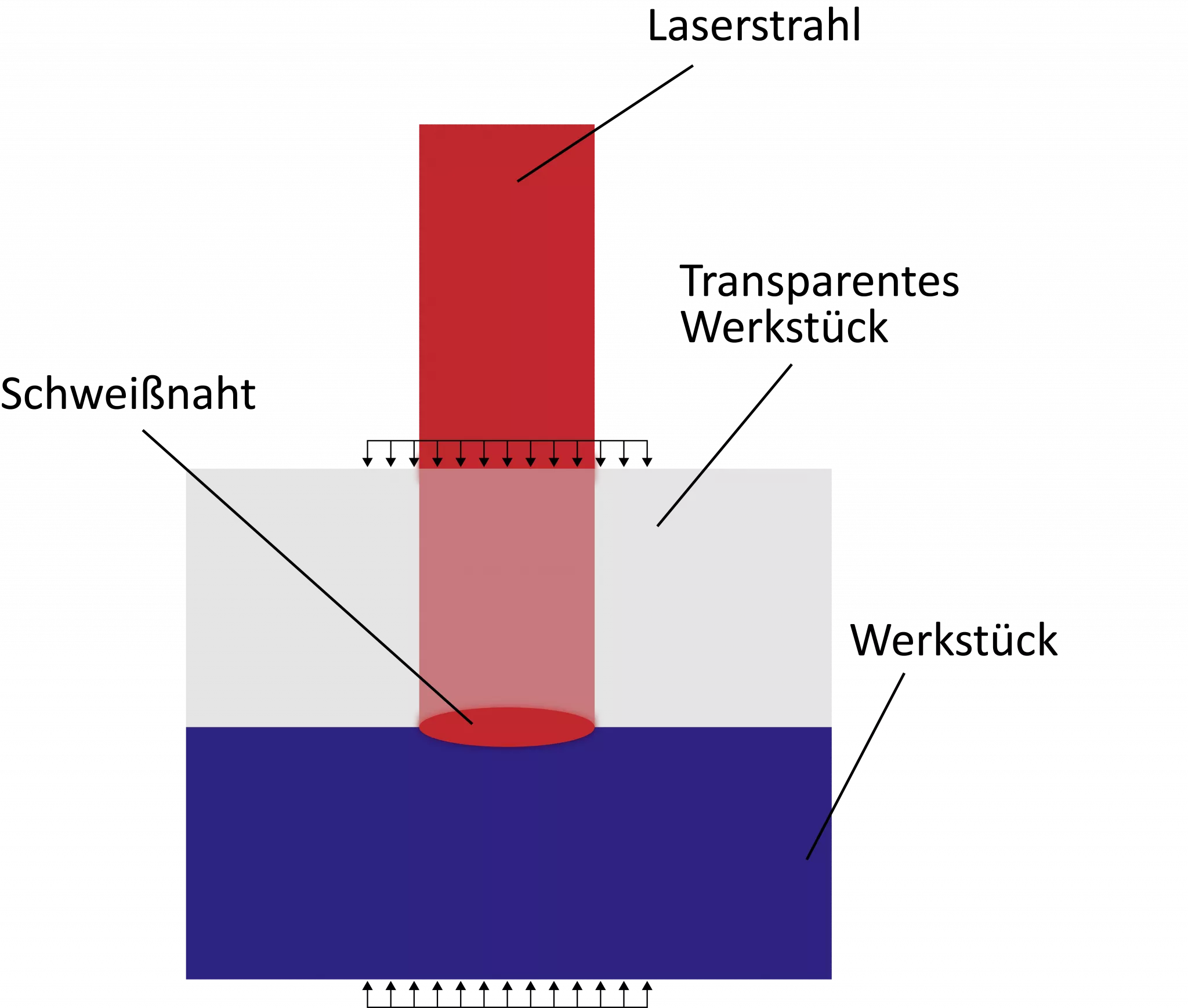
Depending on the way in which the heat acts on the plastic to be welded, different types of plastic welding can be distinguished. In industrial series production, hot plate welding is primarily used. In this welding process, the heating and joining processes can take place separately, as the two joining partners are first heated separately using a heating element and only then joined under pressure after the heating element has been removed. Alternatively, infrared welding is often used in industrial production: in this form of plastic welding, the surfaces of the joining partners to be processed are heated using infrared radiation. Only then is the connection made. A third variant of plastic welding used in industry is laser welding. Here, the joining partners are heated locally using laser light. This process has the advantage of a very low, but at the same time very accurate heat input. As a result, components are damaged less and a particularly high welding speed is achieved. Laser beam welding and infrared welding are also sometimes combined with each other. If one of the two joining partners has a rotatable shape, rotational friction welding is also an option: as one joining partner rotates while the other remains stationary, heat is generated due to the friction, which in turn enables welding. Other variants of plastic welding include ultrasonic welding, vibration welding and circular welding.
Advantages and disadvantages of plastic welding
For many plastics that cannot be permanently bonded together, there is no alternative to plastic welding. It is important to ensure that the welding temperature is suitable and that the plastics to be joined are of the same type. As each plastic has its own chemical composition, it is generally not possible to create permanent joints between joining partners made of different plastics using plastic welding. In addition, any pre-treatments must be carried out on the surfaces of the joining partners during plastic welding. Particular attention must also be paid to the correct welding temperatures: while polystyrene requires a temperature of 270°C to 310°C, polypropylene only requires a temperature of between 230°C and 280°C. If the temperatures during plastic welding exceed the permitted value, the plastics can burn, which not only leads to permanent damage to the component, but can also impair the reliability of the connection between the joining partners.
The advantages of plastic welding clearly include the fact that the various processes can be used to create permanent connections between components where bonding is not a reliable solution. In addition, many plastic welding options offer short working times, precise results and low stress on the components. This applies in particular to laser welding as a variant of plastic welding.