Mechanical Engineering Wiki / Wire bonding
Wire bonding - a thermocompression process for electronic components
The thermocompression process or thermocompression welding is a fusion welding process that is used in particular for the permanent joining of sensitive electronic components such as wire bonding. Alternative welding processes, which also enable two components to be permanently joined together, are often out of the question in this area for various reasons. One example of this is the laser welding process, which generally generates such high temperatures that electronic components such as chips can be damaged. Thermo-compression welding is different: in principle, it is similar to arc stud welding because it is also a pressure welding process. In thermo-compression welding, however, the contact points on the components themselves are not melted; instead, a wire is used, especially for electronic components. This is where the specific name of the sub-task area "wire bonding" comes from. How exactly the process works and the advantages and difficulties that need to be taken into account are explained below.
How thermocompression welding works during wire bonding
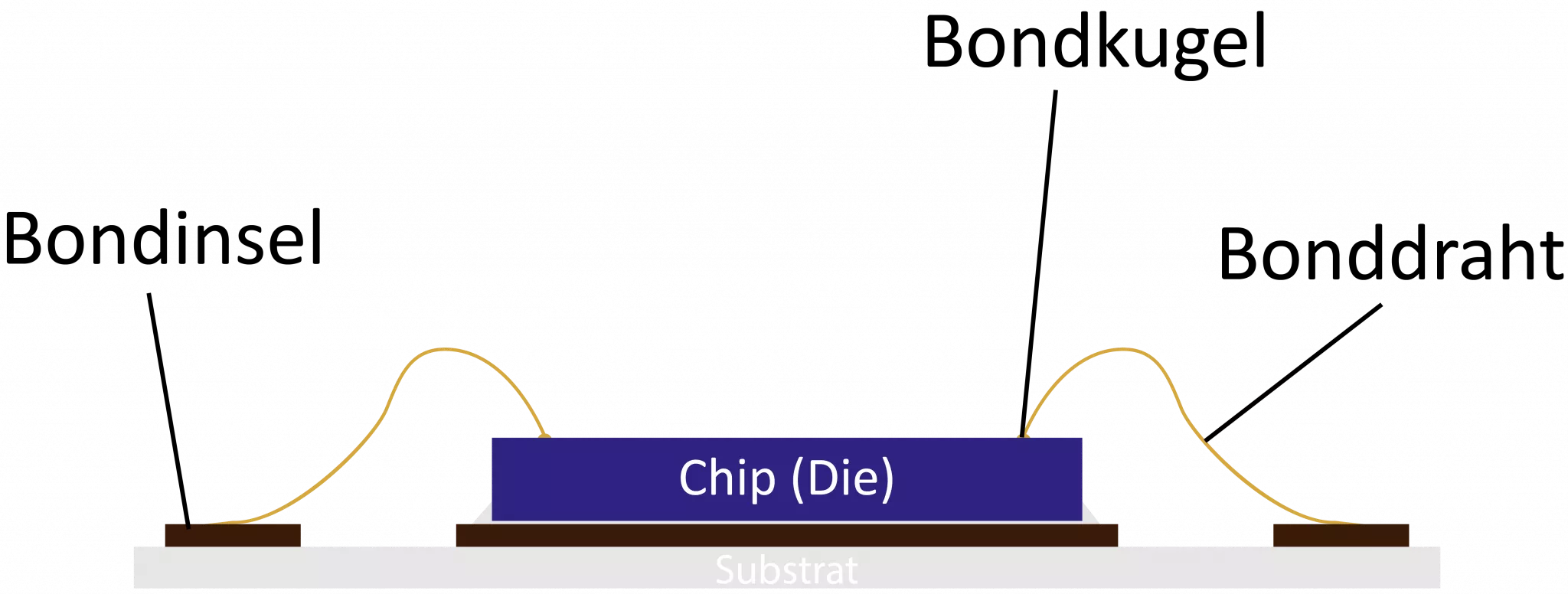
The following explanations relate primarily to thermocompression welding, which is used in the production of electronic components. This is also referred to as wire bonding, which primarily refers to the process in which chips are contacted with the respective housing. To do this, a fine gold wire is first fed through a capillary nozzle and heated from below using a controlled heat source. The heating melts the wire into a ball, which is then pressed onto the contact point during the first weld. This contact point is also known as the bond island.
In order to be able to make a connection with another bonding island or contact point, the capillary nozzle is moved upwards again and brought to the next contact point in a semicircle. There, it is pressed down again and the wire is then cut off. Only fine gold wire is used for thermocompression welding in connection with electronic components or wire bonding. This is processed at temperatures of around 350°C. The advantage of gold wire is that it is resistant to oxidation processes and is therefore suitable for the production of electronic components. Theoretically, it would also be possible to use other materials, but this would only be possible with great technical effort, which is usually not justifiable from a cost perspective.
Advantages and disadvantages of wire bonding as a variant of thermocompression welding
When manufacturing electronic components using thermocompression welding, there are a number of advantages and disadvantages compared to other processes and methods. Compared to the laser welding process, thermocompression welding or wire bonding has the disadvantage of material and tool wear.
On the other hand, the lower working temperatures generated or required for thermocompression welding are more beneficial to the often sensitive components. In addition to the low heat input, other advantages include the short heating times and the fact that the parts joined by thermocompression welding do not suffer any deformation. The strength and durability of the joint is also a positive feature of this process.