Image processing is an established method for measuring and inspecting objects or products (optical quality control), which is based on optical evaluation. Image processing can be used to determine many features simultaneously, very quickly and without contact, which can be used for quality assessment or further processing of the results.
Fundamentals and challenges for optical inspection with the support of image processing
In many industries, optical inspections are very often used directly in the production lines in order to permanently monitor the products at every stage of production and to reject them if necessary. Areas of application are very often found in the automotive supply industry, in mechanical engineering or in medical technology. For cost reasons, it is practically impossible today in series production to have every part produced checked individually by a quality assurance employee, especially as the human error source is one of the biggest causes, and this person does not work with the same reliability on a daily basis.
Image processing is also used in many other areas, such as automated border controls using biometric analysis of people and passports, in the area of police vehicle monitoring to read vehicle license plates or, in the future, as an assistance system in vehicles to recognize traffic signs and automatically adjust speed or to facilitate and automate parking.
The area of 3D image processing is also a rapidly growing market. The famous "reach into the box" is already a reality, even if there is still a lot of development potential here, as the product range is still quite limited. With 3D image processing, depth information can also be obtained by arranging several camera systems at a fixed angle to each other, enabling robot systems, for example, to independently recognize and pick up parts lying on top and exposed in a mesh box.
As you can see, there are almost no limits to the areas of application and the systems are becoming increasingly intelligent.
What happens in an image processing station for optical quality control?
In a first step, a so-called trigger is initiated by a higher-level control system, which starts the measurement request on the PC. The image processing software installed on the PC takes an image via a connected digital camera and transfers it back to the software. The evaluation of the image material then begins. Various mathematical algorithms are used to filter out and optimize (pre-process) the interesting parts of the image, which are then evaluated using optical inspection (routines).
Typical standard inspection routines are
Presence check:
An original image feature is taught in and compared with the inspection image for each inspection. This results in a percentage match rateEdge detection:
Body edges in the form of light-dark or color transitions are detected and measured in the . This is suitable for determining distance or positionPosition control and tracking:
Objects are taught in as object contours using the edge contrasts. The system then automatically recognizes the shape and position of the part and can use the position to track connected systems such as robots so that the part can be gripped regardless of its position.Optical character recognition (OCR):
Independent recognition of text information in the camera image and conversion into normal text for further processingOptical character verification (OCV):
A modification of the OCR function, where a 1:1 comparison of text information is made against a fixed specificationBarcode/2D code recognition:
Reading of various code types of all kinds
The basic structure of an optical test station includes
A monochrome or color digital camera that can be connected to a PC
Suitable lighting to ensure that the products to be tested are always uniformly and homogeneously illuminated (usually LED technology)
Evaluation PC
Image processing software for further processing and evaluation of the image material
Our expertise in the field of image processing for optical quality control
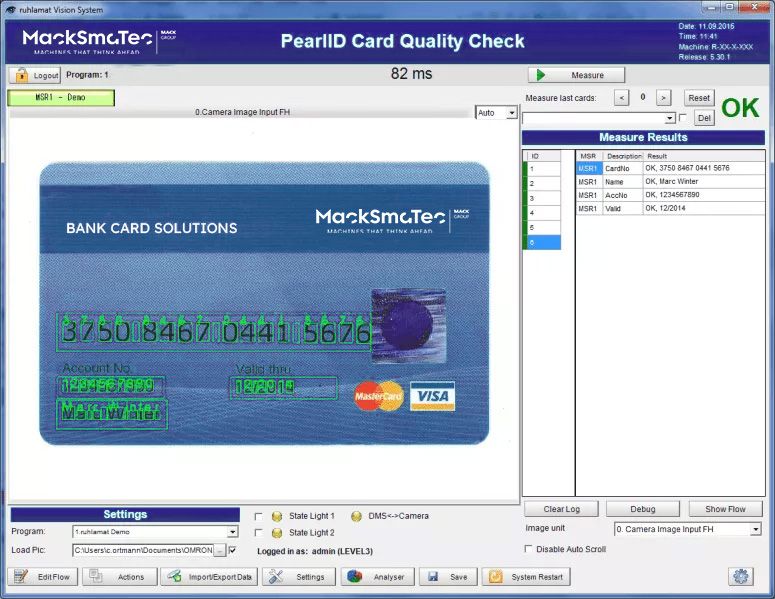
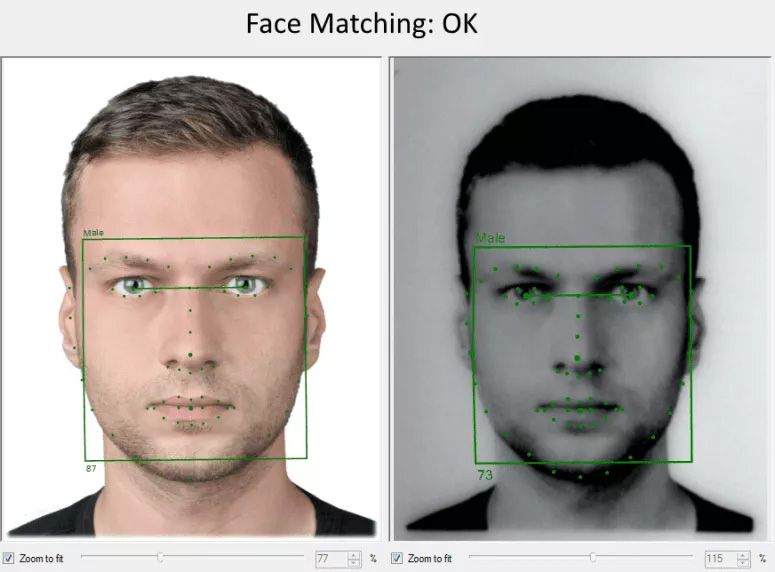
MackSmaTec has many years of extensive expertise in the field of image processing. The production of ID cards and passports in particular poses a major challenge in many respects, as standard algorithms cannot always be used here. For example, chip card production requires very fast processes for the optical verification of personalized texts. A particular difficulty here is the need to be able to compare international characters such as Cyrillic, Greek and Arabic quickly and with a high degree of certainty. At the same time, ease of use for the operator must not be neglected. Biometric evaluation algorithms for comparing personalized passport photos with text data is also a special area.

The difficulties of image processing in optical testing
Optical design is generally one of the greatest difficulties in image processing. Depending on the product, for example, suitable lighting must be found so that there are no nasty surprises in terms of reliability later on. It is therefore extremely important to illuminate the product correctly and consistently (homogeneously). Reflections on the measurement objects are often undesirable and must be avoided. The market offers a wide range of special LED lighting, but the choice is often not trivial and should be left to a specialist.
Certain product groups are also difficult. These include the area of natural products: wood, leather or the processing of fruit, vegetables and fruit is still one of the biggest challenges, as the variety and properties vary greatly here.
Are you interested in the topic of image processing in connection with optical quality controls or inspection stations? Then get in touch with us, we will be happy to help you!


